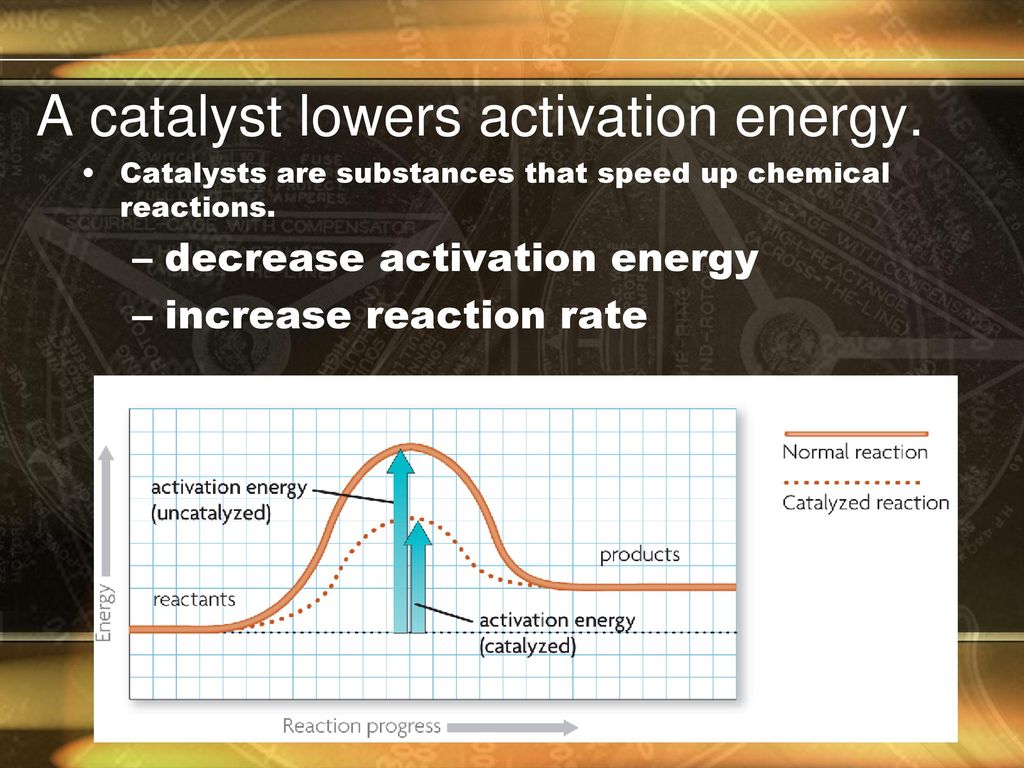
A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27 . The relationship between the rate of the reaction and the activation energy is logk =− ea 2.303rt. Since the activation energy is the difference. One possible way of doing this. This graph compares potential energy. catalysts and activation energy. Lowering the activation energy of a reaction by a catalyst. To increase the rate of a reaction you need to increase the number of successful collisions. as can be seen from the arrhenius equation, the magnitude of the activation energy, \(e_a\), determines the value of the rate. The reaction then goes through a different pathway/mechanism than. a catalyst lowers the activation energy of a certain reaction at \( 27^{\circ} \mathrm{c} \) from 75 to \( 29. a catalyst lowers the activation energy by changing the transition state of the reaction. the catalyst lowers the energy of the transition state for the reaction.
from slideplayer.com
a catalyst lowers the activation energy by changing the transition state of the reaction. The relationship between the rate of the reaction and the activation energy is logk =− ea 2.303rt. Lowering the activation energy of a reaction by a catalyst. The reaction then goes through a different pathway/mechanism than. To increase the rate of a reaction you need to increase the number of successful collisions. This graph compares potential energy. as can be seen from the arrhenius equation, the magnitude of the activation energy, \(e_a\), determines the value of the rate. the catalyst lowers the energy of the transition state for the reaction. Since the activation energy is the difference. One possible way of doing this.
Enzymes. ppt download
A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27 the catalyst lowers the energy of the transition state for the reaction. a catalyst lowers the activation energy of a certain reaction at \( 27^{\circ} \mathrm{c} \) from 75 to \( 29. This graph compares potential energy. the catalyst lowers the energy of the transition state for the reaction. One possible way of doing this. The reaction then goes through a different pathway/mechanism than. as can be seen from the arrhenius equation, the magnitude of the activation energy, \(e_a\), determines the value of the rate. The relationship between the rate of the reaction and the activation energy is logk =− ea 2.303rt. a catalyst lowers the activation energy by changing the transition state of the reaction. catalysts and activation energy. Lowering the activation energy of a reaction by a catalyst. To increase the rate of a reaction you need to increase the number of successful collisions. Since the activation energy is the difference.
From www.labunlimited.com
Solid Phase Catalysis in Continuous Flow Chemistry Lab Unlimited A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27 Since the activation energy is the difference. This graph compares potential energy. a catalyst lowers the activation energy by changing the transition state of the reaction. Lowering the activation energy of a reaction by a catalyst. catalysts and activation energy. To increase the rate of a reaction you need to increase the number of successful collisions. as. A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27.
From chem.libretexts.org
12.2 Catalytic Hydrogenation Chemistry LibreTexts A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27 a catalyst lowers the activation energy of a certain reaction at \( 27^{\circ} \mathrm{c} \) from 75 to \( 29. Lowering the activation energy of a reaction by a catalyst. To increase the rate of a reaction you need to increase the number of successful collisions. a catalyst lowers the activation energy by changing the transition state of. A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27.
From www.chegg.com
Solved A catalyst lowers the activation energy by reaction A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27 catalysts and activation energy. as can be seen from the arrhenius equation, the magnitude of the activation energy, \(e_a\), determines the value of the rate. the catalyst lowers the energy of the transition state for the reaction. a catalyst lowers the activation energy by changing the transition state of the reaction. This graph compares potential energy.. A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27.
From slideplayer.com
A catalyst lowers activation energy. ppt download A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27 The relationship between the rate of the reaction and the activation energy is logk =− ea 2.303rt. This graph compares potential energy. Lowering the activation energy of a reaction by a catalyst. To increase the rate of a reaction you need to increase the number of successful collisions. One possible way of doing this. Since the activation energy is the. A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27.
From byjus.com
39. A catalyst lowers the activation energy of a reaction from 20 kJ A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27 This graph compares potential energy. a catalyst lowers the activation energy of a certain reaction at \( 27^{\circ} \mathrm{c} \) from 75 to \( 29. catalysts and activation energy. One possible way of doing this. the catalyst lowers the energy of the transition state for the reaction. Since the activation energy is the difference. To increase the. A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27.
From www.numerade.com
Suppose that a catalyst lowers the activation barrier of a reaction A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27 a catalyst lowers the activation energy by changing the transition state of the reaction. as can be seen from the arrhenius equation, the magnitude of the activation energy, \(e_a\), determines the value of the rate. One possible way of doing this. The relationship between the rate of the reaction and the activation energy is logk =− ea 2.303rt.. A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Mechanisms of Catalytic Reactions and Characterization of A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27 One possible way of doing this. The relationship between the rate of the reaction and the activation energy is logk =− ea 2.303rt. catalysts and activation energy. a catalyst lowers the activation energy by changing the transition state of the reaction. To increase the rate of a reaction you need to increase the number of successful collisions. The. A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27.
From byjus.com
a catalyst lowers the activation energy of a certain reaction from 75 A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27 Since the activation energy is the difference. To increase the rate of a reaction you need to increase the number of successful collisions. catalysts and activation energy. This graph compares potential energy. The relationship between the rate of the reaction and the activation energy is logk =− ea 2.303rt. as can be seen from the arrhenius equation, the. A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27.
From www.sliderbase.com
Catalysis Presentation Chemistry A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27 Lowering the activation energy of a reaction by a catalyst. The relationship between the rate of the reaction and the activation energy is logk =− ea 2.303rt. The reaction then goes through a different pathway/mechanism than. the catalyst lowers the energy of the transition state for the reaction. This graph compares potential energy. catalysts and activation energy. To. A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27.
From nesslabs.com
Activation energy the chemistry of getting started Ness Labs A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27 The reaction then goes through a different pathway/mechanism than. Lowering the activation energy of a reaction by a catalyst. This graph compares potential energy. as can be seen from the arrhenius equation, the magnitude of the activation energy, \(e_a\), determines the value of the rate. a catalyst lowers the activation energy of a certain reaction at \( 27^{\circ}. A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27.
From www.meritnation.com
a catalyst lowers the activation energy for a certain reaction from 83 A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27 the catalyst lowers the energy of the transition state for the reaction. a catalyst lowers the activation energy by changing the transition state of the reaction. To increase the rate of a reaction you need to increase the number of successful collisions. This graph compares potential energy. catalysts and activation energy. The reaction then goes through a. A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27.
From www.sliderbase.com
Enzymes. A Cell's Catalysts Presentation Biology A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27 The reaction then goes through a different pathway/mechanism than. catalysts and activation energy. the catalyst lowers the energy of the transition state for the reaction. One possible way of doing this. This graph compares potential energy. Since the activation energy is the difference. a catalyst lowers the activation energy by changing the transition state of the reaction.. A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Reaction Rates (Chapter 13) PowerPoint Presentation, free A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27 One possible way of doing this. The relationship between the rate of the reaction and the activation energy is logk =− ea 2.303rt. The reaction then goes through a different pathway/mechanism than. a catalyst lowers the activation energy of a certain reaction at \( 27^{\circ} \mathrm{c} \) from 75 to \( 29. a catalyst lowers the activation energy. A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27.
From www.chegg.com
Solved QUESTION 4 A catalyst I) lowers activation energy A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27 Lowering the activation energy of a reaction by a catalyst. Since the activation energy is the difference. as can be seen from the arrhenius equation, the magnitude of the activation energy, \(e_a\), determines the value of the rate. a catalyst lowers the activation energy of a certain reaction at \( 27^{\circ} \mathrm{c} \) from 75 to \( 29.. A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27.
From slideplayer.com
Enzymes. ppt download A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27 This graph compares potential energy. catalysts and activation energy. a catalyst lowers the activation energy of a certain reaction at \( 27^{\circ} \mathrm{c} \) from 75 to \( 29. the catalyst lowers the energy of the transition state for the reaction. The relationship between the rate of the reaction and the activation energy is logk =− ea. A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27.
From www.youtube.com
The energy of activation for a reaction is `100 KJ mol^(1)`. The A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27 a catalyst lowers the activation energy by changing the transition state of the reaction. the catalyst lowers the energy of the transition state for the reaction. Since the activation energy is the difference. To increase the rate of a reaction you need to increase the number of successful collisions. This graph compares potential energy. One possible way of. A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27.
From www.cheric.org
Chemical Reaction (Reaction rate) A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27 a catalyst lowers the activation energy by changing the transition state of the reaction. This graph compares potential energy. as can be seen from the arrhenius equation, the magnitude of the activation energy, \(e_a\), determines the value of the rate. a catalyst lowers the activation energy of a certain reaction at \( 27^{\circ} \mathrm{c} \) from 75. A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27.
From www.linstitute.net
Edexcel A Level Chemistry复习笔记1.9.3 MaxwellBoltzmann Distributions翰林国际教育 A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27 Lowering the activation energy of a reaction by a catalyst. the catalyst lowers the energy of the transition state for the reaction. Since the activation energy is the difference. The reaction then goes through a different pathway/mechanism than. One possible way of doing this. The relationship between the rate of the reaction and the activation energy is logk =−. A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Certain Reaction At 27.